Abstract
The United States healthcare landscape, particularly in oncology, is undergoing a profound transformation. As treatment paradigms shift towards increasingly personalized therapies, the imperative for equally precise and ethical marketing strategies has never been more critical. This article explores the symbiotic relationship between precision medicine’s established methodologies and the emergent field of precision marketing, specifically within the complex and highly regulated realm of oncology in the US. We delve into how artificial intelligence (AI) is serving as the primary catalyst, revolutionizing how pharmaceutical companies engage with healthcare professionals (HCPs) and ultimately, improve patient outcomes. Drawing parallels between the stratification of patient populations in precision medicine and the segmentation of HCPs in precision marketing, we will examine the ethical considerations, data privacy challenges, and technological advancements driving this evolution. This analysis aims to provide actionable insights for pharma managers and medical professionals, illustrating how a data-driven, AI-powered approach can optimize resource allocation, enhance message relevance, and foster more meaningful engagements, thereby aligning marketing efforts with the patient-centric ethos of modern oncology. We will present five visual representations to underscore key trends and illustrate the potential of precision marketing models.
Introduction: The Dawn of a Data-Driven Era in Oncology
For decades, pharmaceutical marketing often relied on broad strokes, casting wide nets in the hope of capturing the attention of a diverse medical community. However, the 21st century has ushered in an era of unprecedented specialization, particularly within oncology. The Human Genome Project, coupled with exponential advancements in molecular biology, has propelled medicine into a “precision” age, where treatments are increasingly tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup, tumor characteristics, and unique biological profile. This paradigm shift, epitomized by precision medicine, has delivered remarkable successes, transforming previously untreatable cancers into manageable conditions and significantly improving quality of life for countless patients.
Yet, while oncology treatments have become remarkably precise, the marketing strategies employed to communicate these innovations often lag. In a crowded therapeutic landscape, where groundbreaking discoveries are commonplace, the challenge for pharma companies is no longer merely to develop innovative treatments, but to effectively and efficiently communicate their value to the right HCPs at the right time. This is where the lessons from precision medicine become invaluable, offering a blueprint for a more sophisticated, data-driven approach to marketing – an approach we term “precision marketing.”
The US oncology market, characterized by its dynamism, diverse stakeholders, and stringent regulatory environment, serves as an ideal crucible for examining this evolution. Here, the sheer volume of scientific data, the rapid pace of drug development, and the varying preferences of HCPs necessitate a departure from traditional marketing playbooks. Artificial intelligence stands at the forefront of this revolution, transforming raw data into actionable insights and enabling a level of personalization previously unimaginable. This article will explore how AI is not just optimizing existing marketing processes but fundamentally redefining them, creating a more ethical, efficient, and impactful engagement model for the benefit of patients and the entire healthcare ecosystem.
The Pillars of Precision Medicine: A Framework for Marketing
Precision medicine, at its core, is built upon several foundational principles:
- Patient Stratification: Identifying distinct subgroups of patients who share common biological characteristics or disease pathways.
- Biomarker-Driven Diagnostics: Utilizing specific molecular markers to guide treatment decisions and predict therapeutic response.
- Personalized Therapies: Developing and administering treatments precisely tailored to these identified patient subgroups.
- Continuous Data Analysis & Feedback Loops: Iteratively refining diagnostic and therapeutic approaches based on real-world outcomes.
These principles, while originating in clinical science, offer a powerful analogue for transforming pharmaceutical marketing in oncology.
1. Patient Stratification to HCP Segmentation: Knowing Your Audience
Just as precision medicine stratifies patients based on biological markers, precision marketing stratifies HCPs based on a multitude of digital and behavioral markers. In oncology, HCPs are not a monolithic group. They vary significantly in their:
- Specialization: Medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, surgical oncologists, pathologists, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, etc.
- Practice Setting: Academic medical centers, community hospitals, private practices, research institutions.
- Patient Volume & Caseload: The number and types of cancer patients they treat.
- Digital Engagement Preferences: How they consume information (journals, webinars, conferences, medical news sites, social media, peer networks).
- Therapeutic Adoption Patterns: Their willingness to adopt new therapies, prescribe off-label, or participate in clinical trials.
- Geographic Location: Regional prevalence of certain cancer types, access to specialized facilities.
- Peer Influence & Key Opinion Leader (KOL) Status: Their role in shaping the opinions and practices of others.
AI algorithms can ingest and analyze vast datasets encompassing these variables – from claims data and prescribing patterns to digital interaction histories and professional affiliations – to create highly granular HCP segments. This allows pharma marketers to move beyond demographic targeting to psychographic and behavioral targeting, understanding not just who an HCP is, but how they think and what information they need.
2. Biomarker-Driven Diagnostics to Digital Behavioral Signals:
- Unlocking Insights: In precision medicine, biomarkers provide objective, measurable indicators of disease status and treatment response. In precision marketing, “digital behavioral signals” serve an analogous function. Every interaction an HCP has with digital content – a click on an email, a download of a clinical trial abstract, participation in a virtual advisory board, engagement with a medical society’s social media post – generates a data point. When aggregated and analyzed by AI, these signals become powerful indicators of:
- Information Needs: What therapeutic areas, drug mechanisms, or patient profiles an HCP is actively researching.
- Engagement Propensity: Which channels (email, webinar, sales representative visit) they are most responsive to.
- Knowledge Gaps: Areas where they may require further education or clarification regarding a new therapy.
- Prescribing Intent: Early indicators of potential interest in adopting a new drug.
Natural Language Processing (NLP), a subfield of AI, can further analyze unstructured data from medical forums, academic papers, and social media to gauge sentiment, identify emerging trends, and understand the language HCPs use to discuss specific treatments and patient challenges. This provides a rich, dynamic “diagnostic” picture of each HCP’s evolving needs and preferences.
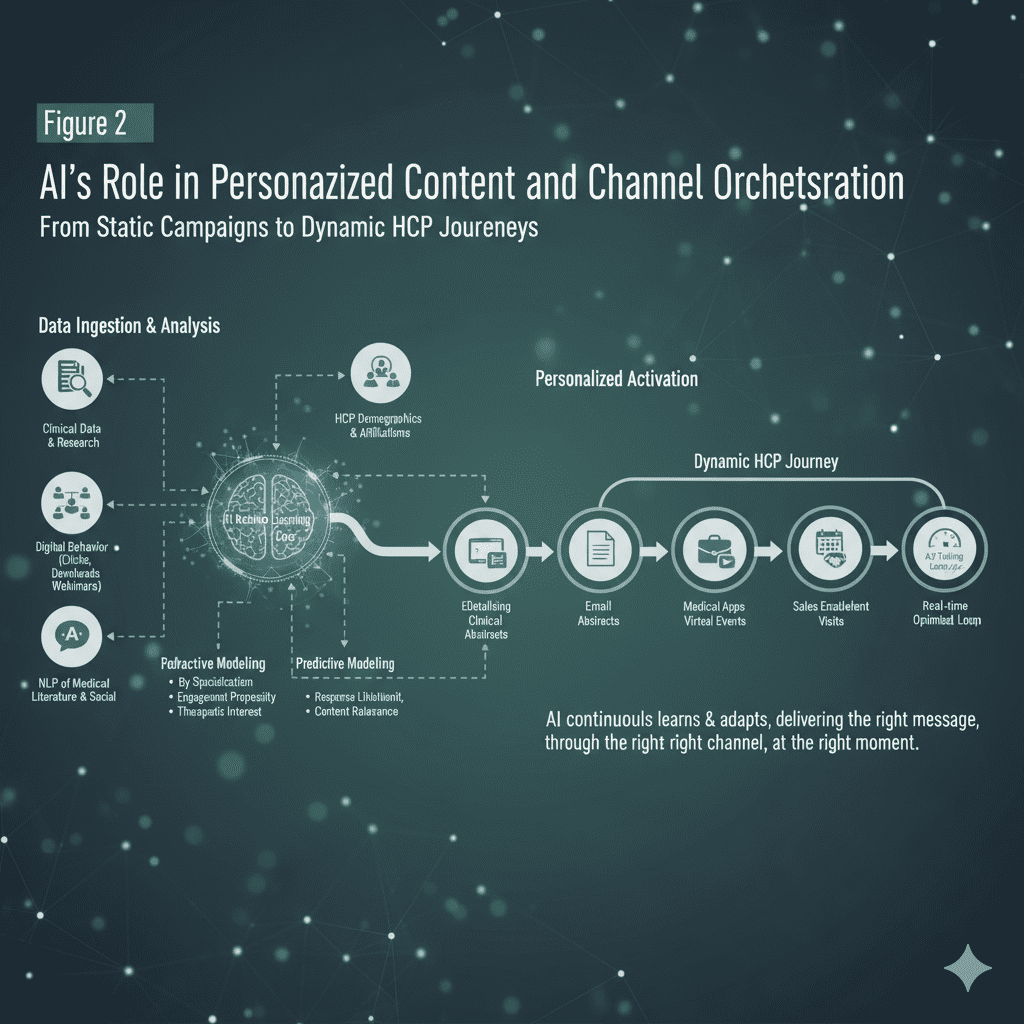
3. Personalized Therapies to Tailored Content and Channel Orchestration
The ultimate goal of precision medicine is to deliver the right treatment to the right patient at the right time. Precision marketing aims for the right message delivered through the right channel to the right HCP at the right moment.
AI-powered marketing automation platforms enable this level of personalization at scale. Once HCP segments are defined and their digital behavioral signals understood, AI can dynamically:
- Generate Tailored Content: Recommending relevant clinical data, patient case studies, dosing information, or competitive analyses based on an HCP’s specific interests and prior interactions. For instance, an oncologist primarily treating lung cancer might receive targeted information on a new ALK inhibitor, while a hematologist would receive updates on CAR T-cell therapies.
- Optimize Channel Mix: Determining the most effective way to reach an HCP – be it a personalized email, an invitation to a targeted webinar, a notification within a medical app, or even informing a sales representative about the most opportune time for a personal visit, armed with specific conversation starters.
- Adaptive Nurturing Journeys: Creating dynamic communication pathways that adapt in real-time based on an HCP’s engagement. If an HCP opens an email but doesn’t click a link, a follow-up with a different format or angle might be triggered. If they download a white paper, they might be enrolled in a deeper engagement track.
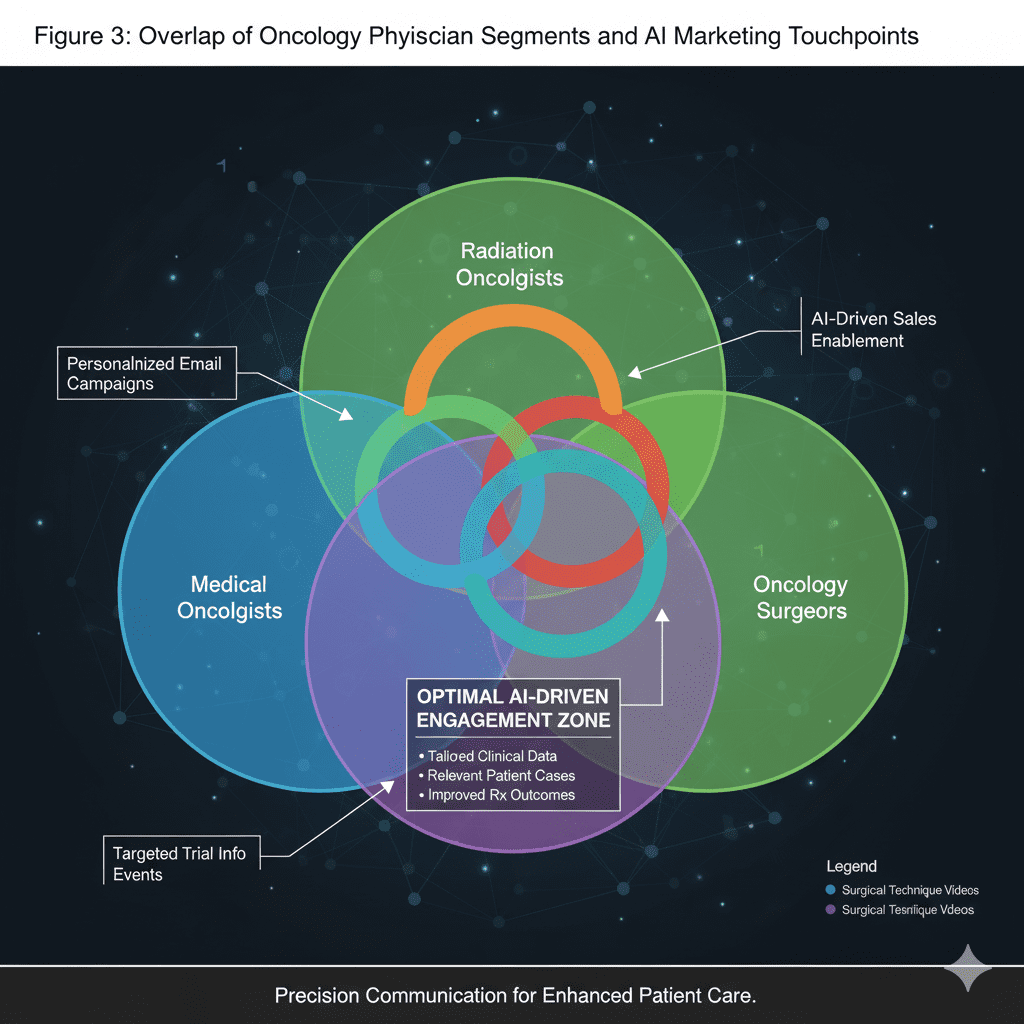
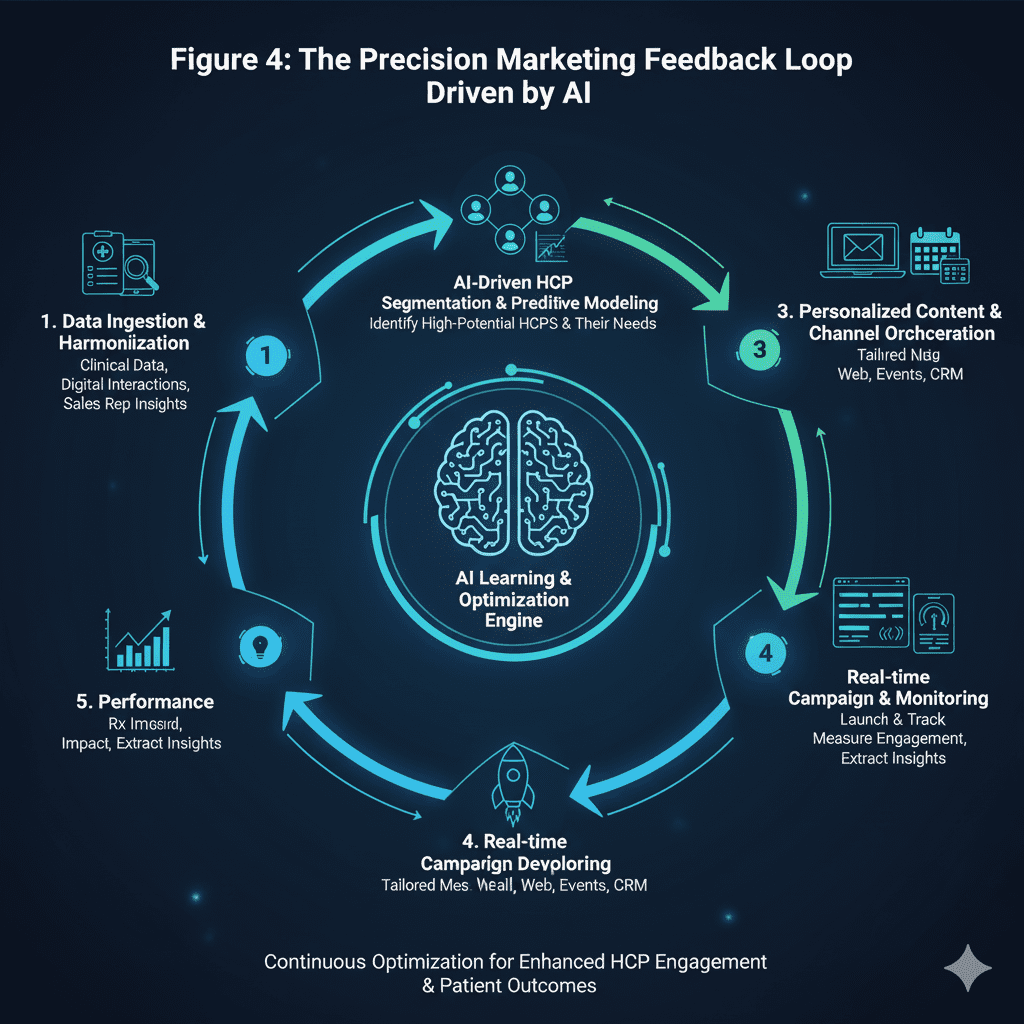
4. Continuous Data Analysis & Feedback Loops: The Learning Marketing Engine
Just as clinical trials and real-world evidence continuously refine medical practice, precision marketing thrives on continuous data analysis and feedback. AI systems are not static; they are learning engines. Through techniques like machine learning and predictive analytics, they continuously:
- Monitor Campaign Performance: Tracking open rates, click-through rates, content downloads, webinar attendance, and ultimately, prescribing behaviors.
- Identify Causal Relationships: Understanding which messages, channels, and timings lead to the most impactful HCP engagement and therapeutic adoption.
- Predict Future Behaviors: Forecasting which HCPs are most likely to adopt a new therapy, based on their past interactions and similarity to successful adopters.
- A/B Test at Scale: Continuously testing different headlines, calls to action, image choices, and message lengths across various segments to identify optimal performance.
This iterative process creates a virtuous cycle: more data leads to better insights, which leads to more effective personalization, which generates more data for further refinement. The result is a marketing engine that not only optimizes campaigns in real-time but also continually learns and improves its understanding of the oncology HCP audience.
The AI Revolution: Catalyzing Precision Marketing in Oncology
Artificial intelligence is not merely an enhancer of existing marketing strategies; it is a fundamental disruptor, reshaping every facet of how pharmaceutical companies engage with oncology HCPs. Its capabilities extend far beyond simple automation, enabling unprecedented levels of analysis, personalization, and predictive power.
1. Data Aggregation and Harmonization: The Foundation
The first and often most challenging step in precision marketing is the effective aggregation and harmonization of disparate data sources. In oncology marketing, this data deluge includes:
- Prescribing Data: Anonymized claims data detailing drug utilization patterns by HCPs.
- Medical & Scientific Literature: Journals, clinical trial databases (e.g., ClinicalTrials.gov), conference proceedings.
- Digital Engagement Data: Website visits, email opens/clicks, webinar attendance, content downloads, social media interactions, virtual conference participation.
- CRM Data: Records from sales representative interactions, notes, and visit summaries.
- Third-Party Data: Professional affiliations, demographic information, practice profiles, and public health data.
AI, particularly machine learning algorithms, excels at ingesting these massive, varied datasets, cleaning them, identifying patterns, and linking them to create a unified, 360-degree view of each HCP. This foundational capability is crucial, as fragmented data leads to incomplete insights and suboptimal personalization.
2. Predictive Analytics: Forecasting Future Behavior
One of AI’s most powerful contributions to precision marketing is its ability to move beyond descriptive analysis (“what happened”) to predictive analysis (“what will happen”). In oncology, predictive models can forecast:
- Likelihood of Adopting New Therapies: Identifying HCPs most likely to prescribe a new oncology drug upon its launch or after a specific educational intervention, based on their past adoption patterns for similar innovations.
- Response to Different Channels: Predicting whether an HCP is more likely to respond to an email, a virtual event invitation, or a visit from a medical science liaison (MSL).
- Churn Risk: Identifying HCPs who might be disengaging or shifting their prescribing habits away from a particular therapy, allowing for proactive intervention.
- Patient Volume Growth: Estimating the potential for growth in specific oncology patient segments within an HCP’s practice, guiding resource allocation.
These predictions enable pharma managers to allocate marketing resources more efficiently, focusing efforts on high-potential HCPs with tailored strategies, rather than employing a scattergun approach.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP): Understanding the Nuances
NLP allows AI to understand, interpret, and generate human language. In oncology marketing, NLP is transformative for:
- Content Analysis: Sifting through vast amounts of medical literature, clinical trial results, and real-world evidence to identify key insights and tailor summaries for specific HCP segments. It can even help identify gaps in existing content.
- Sentiment Analysis: Monitoring medical forums, professional social media groups, and feedback channels to gauge HCP sentiment towards specific therapies, competitors, or disease management strategies.
- Sales Enablement: Analyzing transcripts of sales calls or digital interactions to provide sales representatives with immediate feedback on effective messaging, identify common questions, and suggest personalized talking points for future engagements.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Providing immediate, AI-powered responses to HCP queries on product information, dosing, or trial data, ensuring 24/7 access to information.
4. Generative AI: Revolutionizing Content Creation and Optimization
While still an emerging field, generative AI (e.g., large language models) holds immense promise for oncology marketing. It can assist in:
- Drafting Personalized Communications: Generating first drafts of emails, ad copy, or social media posts tailored to specific HCP segments and their known interests.
- Summarizing Complex Clinical Data: Creating digestible summaries of lengthy clinical trial reports for different audiences, from general practitioners to specialized oncologists.
- Developing Educational Modules: Assisting in the creation of interactive learning content based on an HCP’s specific knowledge gaps.
It’s crucial to note that human oversight remains paramount, especially in a highly regulated field like pharma, to ensure accuracy, compliance, and ethical content generation. AI assists; it does not replace the human touch and medical expertise.
5. Ethical AI and Data Privacy: Navigating the Regulatory Landscape
The power of AI in precision marketing comes with significant responsibilities, particularly within the US healthcare context. Pharma companies must adhere to stringent regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and state-specific data privacy laws.
- Anonymization and De-identification: All patient data used to inform HCP segmentation must be rigorously anonymized or de-identified to protect patient privacy. AI algorithms can assist in this process but must be implemented with robust safeguards.
- Transparency and Consent: While HCPs are not patients, transparency regarding data collection and usage, particularly for personalized outreach, fosters trust.
- Bias Detection and Mitigation: AI models can inadvertently perpetuate or even amplify biases present in their training data. In oncology, this could lead to under-serving certain demographics or over-targeting others. Regular auditing of AI algorithms for bias is essential to ensure equitable and ethical marketing practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Every piece of communication generated or optimized by AI must still pass through traditional medical, legal, and regulatory (MLR) review processes to ensure accuracy, claims substantiation, and compliance with FDA and other guidelines.
Pharma managers must invest in robust data governance frameworks, cybersecurity measures, and compliance teams to ensure that AI-driven precision marketing operates within legal and ethical boundaries.
Practical Implications and Actionable Insights for Pharma Managers
For pharma managers operating in the US oncology market, the shift to precision marketing, driven by AI, is not optional – it’s an imperative for sustained success and ethical engagement. Here are actionable insights:
- Invest in a Unified Data Infrastructure: The first step is to break down data silos. Implement a robust Customer Data Platform (CDP) or similar solution that can aggregate, clean, and harmonize all HCP interaction data from various sources (CRM, marketing automation, digital analytics, third-party data). This forms the single source of truth for AI.
- Build or Partner for AI Expertise: Develop in-house AI and data science capabilities or partner with specialized vendors who understand the nuances of healthcare data and regulations. This isn’t just about software; it’s about the talent to build, manage, and interpret AI models.
- Prioritize HCP Journey Mapping: Understand the complex journeys HCPs undertake from initial awareness of a new therapy to eventual adoption. Use AI to identify key touchpoints, information needs, and decision drivers at each stage, then design personalized content and channel strategies accordingly.
- Embrace a Test-and-Learn Culture: Precision marketing is iterative. Encourage continuous A/B testing of messaging, channels, and timing. Utilize AI to quickly analyze results and optimize campaigns in real-time. Failure in a small test
Failure in a small test provides valuable learning that prevents larger campaign failures.
Focus on Value, Not Just Volume: With AI, the goal is not to send more messages, but to send more relevant messages. Shift KPIs from raw impressions or email opens to engagement quality, content consumption, and ultimately, impact on prescribing behavior and patient outcomes.
Integrate Sales and Marketing: AI insights should empower both marketing and sales teams. Provide sales representatives with AI-generated “next best action” recommendations, personalized talking points, and insights into an HCP’s digital engagement, transforming them into highly informed scientific communicators. This “AI-enhanced sales enablement” closes the loop between digital and in-person interactions.
Champion Ethical AI and Data Governance: Establish clear guidelines for data collection, usage, and privacy. Regularly audit AI models for bias and ensure full compliance with HIPAA and other regulatory frameworks. Build trust with HCPs by being transparent about how their professional engagement data is used to enhance their experience.
Measure Beyond ROI: Impact on Patient Outcomes: While ROI remains important, precision marketing in oncology should ultimately be measured by its ability to facilitate better patient care. This includes tracking indicators like faster diagnosis rates (where marketing supports awareness of diagnostic tools), improved adherence (where HCP education supports patient counseling), and appropriate utilization of advanced therapies.
Conclusion: The Symbiosis of Precision and Purpose
The parallels between precision medicine and precision marketing are more than just a convenient analogy; they represent a fundamental alignment of purpose. Both paradigms are driven by data, powered by advanced analytics, and aimed at optimizing outcomes through targeted, personalized interventions. In the US oncology market, where every decision carries immense weight, this shift is not merely an option—it is an ethical imperative.
By embracing the principles of precision medicine, pharma marketers can move beyond the broad strokes of traditional campaigns and build a more sophisticated, data-driven engine for engagement. AI is the catalyst that makes this possible, enabling a level of personalization, efficiency, and insight that was previously unimaginable. This transformation is not about replacing human interaction; it’s about making it more meaningful and impactful.
The future of oncology marketing is one where every communication is a targeted intervention, every resource is a tool for better care, and every engagement is a step towards a more informed and effective healthcare ecosystem. The ultimate triumph of precision marketing will not be measured in higher open rates or increased sales, but in its ability to facilitate better clinical decisions and, most importantly, improve the lives of patients facing cancer. By learning from the triumph of precision medicine, pharma can ensure its marketing efforts are not just precise but purposeful.
The Oncodoc team is a group of passionate healthcare and marketing professionals dedicated to delivering accurate, engaging, and impactful content. With expertise across medical research, digital strategy, and clinical communication, the team focuses on empowering healthcare professionals and patients alike. Through evidence-based insights and innovative storytelling, Hidoc aims to bridge the gap between medicine and digital engagement, promoting wellness and informed decision-making.



