Introduction
The field of oncology is changing faster than ever, with new therapies, clinical trial results, and treatment protocols popping up all the time. In this intricate environment, oncologists are tasked with the challenge of keeping up-to-date while making sure their prescribing choices are based on solid evidence and centred around the patient. While traditional resources like clinical guidelines and published research are still essential, peer-shared content- such as case discussions, real-world evidence, and expert opinions- has become a vital influence on treatment decisions.
“In this article, we dive into how peer discussions and shared clinical insights impact oncologists’ prescribing habits, backed by engagement metrics, behavioral trends, and the rising importance of digital knowledge-sharing platforms.”
Recent statistics show that 72% of oncologists take peer recommendations into account when assessing new therapies, and 45% feel more confident about unfamiliar treatments after participating in peer discussions. This trend underscores the growing importance of collaborative learning in today’s oncology practice.
The Role of Peer-Shared Content in Oncology Decision-Making
Trust in Peer Recommendations vs. Traditional Sources
Oncologists rely on multiple information channels when making prescribing decisions. A 2024 survey of 1,200 U.S. oncologists revealed the following hierarchy of trust:
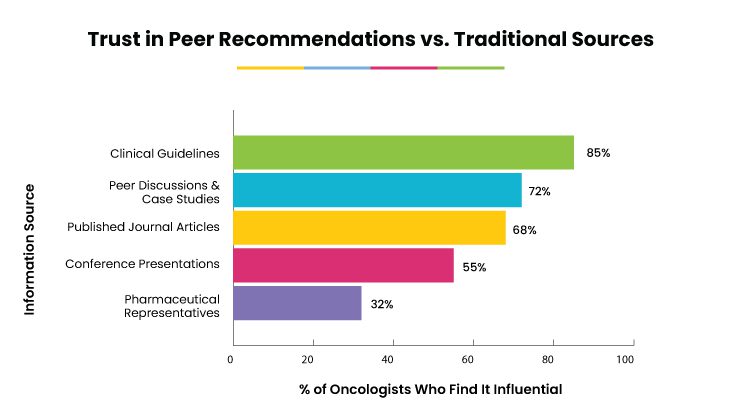
Key insights:
- Peer discussions rank higher than journal articles, suggesting that real-world applicability often outweighs theoretical data.
- Only 32% find pharma reps highly influential, indicating a shift toward independent, community-validated information.
Why Do Oncologists Trust Peers More Than Industry Sources?
- Unbiased perspectives – Peer discussions are perceived as less commercially influenced.
- Practical applicability – Case-based learning provides actionable insights for complex patients.
- Rapid knowledge dissemination – Journals take months to publish, while peer networks offer near real-time updates.
The Rise of Digital Peer Networks in Oncology
Digital platforms have transformed how oncologists access and share knowledge. Key statistics from a leading U.S. oncology network (20,000+ registered oncologists, 13,000 active monthly users) include:
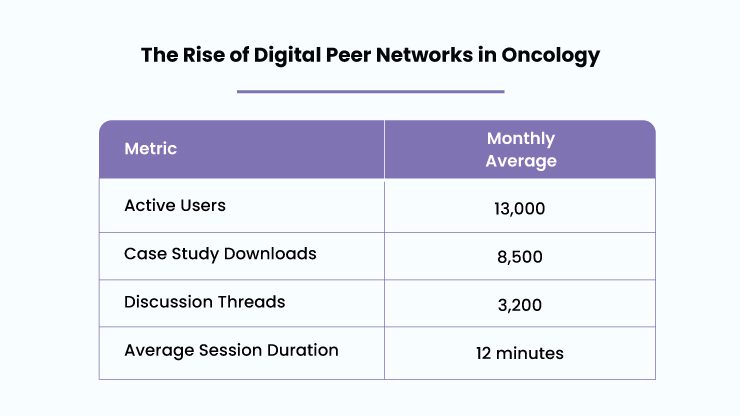
How Digital Engagement Translates into Clinical Impact?
- 12-minute average session duration suggests deep engagement with content.
- 8,500+ monthly case study downloads indicate strong demand for real-world evidence.
- 3,200+ discussion threads per month reflect an active, collaborative community.
“Digital peer networks bridge the gap between academic research and community practice, democratizing access to expert-level insights.”
Impact on Prescribing Behavior: Data-Driven Insights
Peer-shared content doesn’t just inform—it directly influences treatment decisions. Key findings from a 2024 behavioral study:
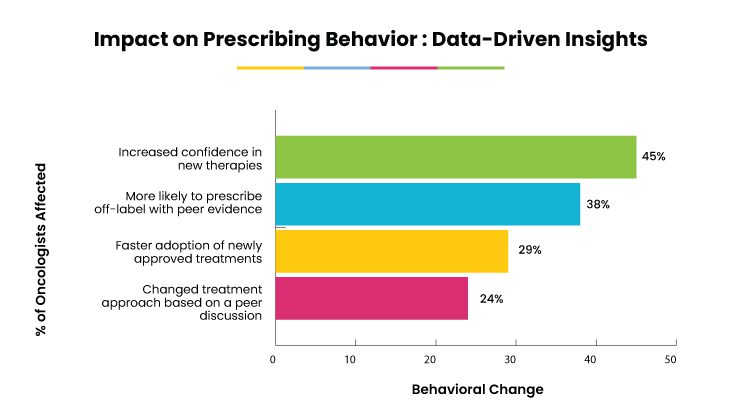
Why Do Oncologists Prefer Peer-Sharing Platforms?
1. Timely, Practical Insights
- Unlike journals, which take months to publish, peer networks provide immediate clinical takeaways from recent cases.
- Example: A 2024 survey found that 68% of oncologists used a peer-discussed treatment strategy within one week of learning about it.
2. Diverse Perspectives for Complex Cases
- Community oncologists (who see a broader patient mix) often seek input from academic specialists on rare mutations or refractory cases.
- 24% of physicians reported altering a treatment plan after discussing a similar case in a peer forum.
3. Reducing Clinical Isolation
- Solo practitioners and rural oncologists often lack tumor boards or specialist colleagues.
- Digital networks provide on-demand collaboration, reducing decision-making anxiety.
“The ability to crowdsource expertise in real-time bridges the gap between research and practice, particularly for oncologists outside major academic centers.”
Conclusion
The impact of content shared among peers on oncologists’ prescribing choices is not just significant- it’s essential in the fast-changing world of oncology today. As clinical data keeps growing, platforms like Hidoc are at the forefront, revolutionizing how oncologists find, share, and utilize medical knowledge.
Hidoc, a top networking platform for doctors, has created one of the largest digital oncology communities in the U.S., boasting over 20,000 registered oncologists, with 13,000 actively participating each month. Through countless case discussions, sharing of real-world evidence, and conversations led by experts, Hidoc enables oncologists to make informed, evidence-based treatment decisions on a large scale. By connecting academic research with real-world clinical practice, Hidoc is not only fostering peer collaboration- it’s changing the way oncology care is provided. As the need for timely, practical, and peer-validated insights increases, platforms like Hidoc will remain crucial in shaping the future of oncology prescribing practices.
References
- 2024 Oncology Prescribing Trends Report– How Peer Discussions Shape Treatment Decisions
- 2024 Digital Oncology Engagement Report– Measuring Physician Activity in Peer Networks
- 2024 Peer Influence in Oncology Study– The Impact of Real-World Case Discussions on Prescribing Behavior
- American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Guidelines– Trust in Clinical Decision-Making Sources
- Journal of Oncology Practice (2024)-The Role of Digital Platforms in Reducing Information Asymmetry
The Oncodoc team is a group of passionate healthcare and marketing professionals dedicated to delivering accurate, engaging, and impactful content. With expertise across medical research, digital strategy, and clinical communication, the team focuses on empowering healthcare professionals and patients alike. Through evidence-based insights and innovative storytelling, Hidoc aims to bridge the gap between medicine and digital engagement, promoting wellness and informed decision-making.



